 简体中文
简体中文
Advantages of SPC-Wood Composite Materials
I. Equipment and Manufacturing Process for SPC-Wood Composites
The composite technology of Stone Plastic Composite (SPC) and wood combines the stability of SPC with the decorative appeal of wood. The core production process includes **substrate preparation, lamination, and surface treatment**, with the following key equipment and techniques:
1. Key Production Equipment
1. SPC Substrate Production Line
Mixing System: High-speed mixer for blending stone powder, PVC resin, stabilizers, etc.
Extruder: Twin-screw extruder for melting and shaping the mixture into SPC sheets.
Calendering/Calibrating Machine: Ensures uniform thickness and smooth surface.
2. Wood Veneer Processing Equipment
Veneer Cutting Machine: Cuts real wood veneer or decorative wood-grain layers.
UV Coating Machine (Optional): Applies UV-cured coatings for enhanced wear resistance.
3. Lamination Equipment
Hot Press Machine: Uses hot-melt or PU adhesive to bond SPC with wood veneer under high temperature and pressure.
Cold Press Machine (Optional): Suitable for low-temperature lamination (e.g., thin wood veneers).
Roll Press Machine: Continuous lamination for large-scale production.
4. Post-Processing Equipment
CNC Cutting Machine: Precision cutting of composite panels.
Surface Treatment Equipment: UV curing, embossing, or texture enhancement for wood-like aesthetics.
2. Key Process Steps
1. SPC Substrate Preparation
Raw material mixing → High-temperature extrusion → Calendering → Cooling → Edge trimming
2. Lamination Process
Hot Press Lamination (Primary Method):
Adhesive application (e.g., PUR hot-melt glue) → Wood veneer bonding → High-pressure pressing (120-180°C) → Cooling
Cold Press Lamination (For Thin Veneers):
Uses eco-friendly adhesives (e.g., water-based PU glue) → Room-temperature pressing
Wood Grain Enhancement**: Digital printing, thermal transfer, or real wood veneer with protective coatings (e.g., UV layer).
Embossing**: Synchronized embossing for a tactile wood-like texture.
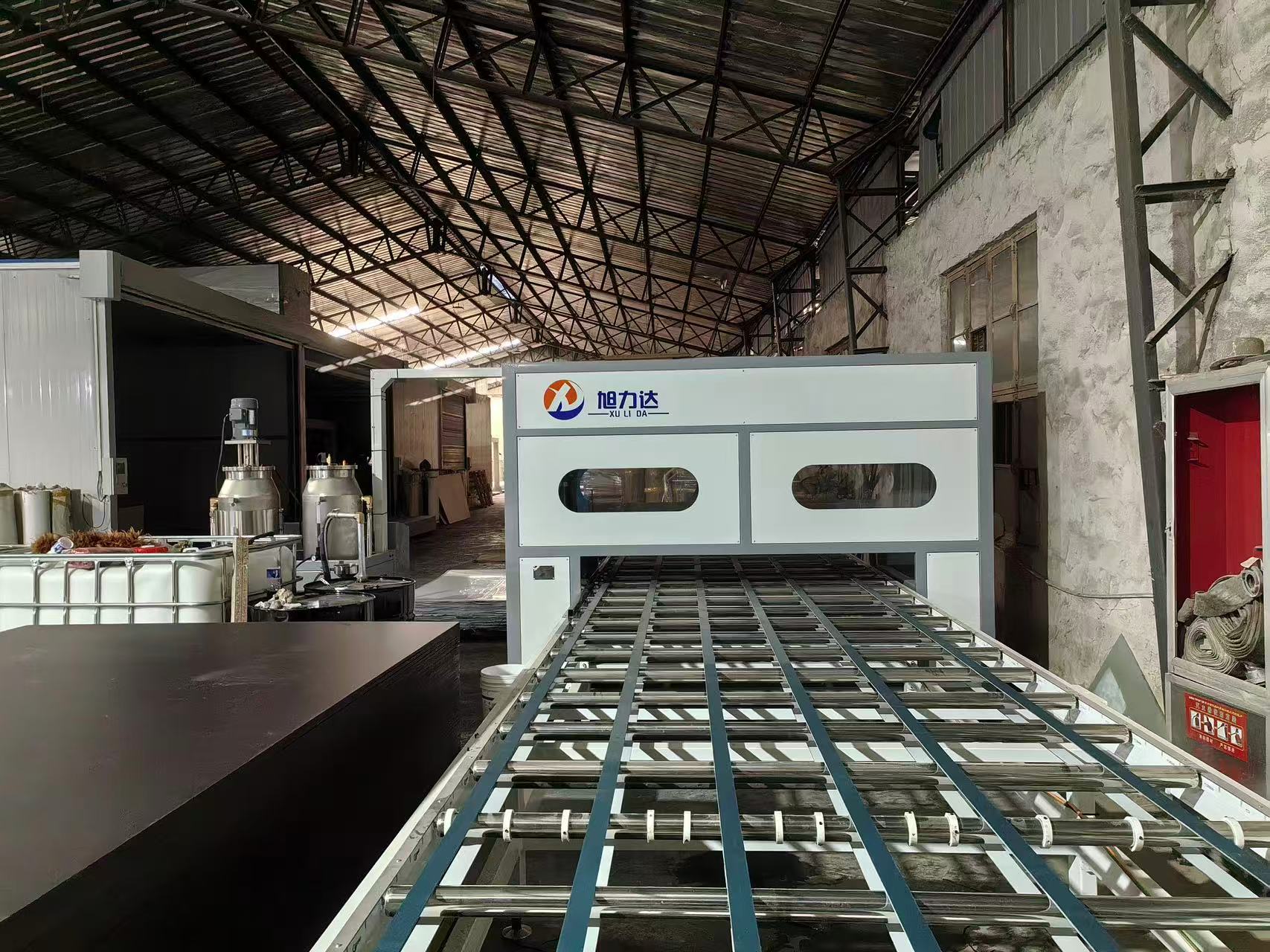

II. Development Prospects of SPC-Wood Composites
1. Market Drivers
Eco-Friendly Demand: Low formaldehyde (ENF-grade), recyclable, replacing traditional laminate/wood flooring.
Performance Benefits: Combines SPC’s waterproof stability with wood’s natural aesthetics, ideal for underfloor heating and commercial spaces.
Policy Support: Green building regulations (e.g., China’s "Dual Carbon" goals, EU CE certification) boost adoption.
2. Technological Trends
Lightweight & High Strength: Nano-modified SPC (e.g., carbon fiber-reinforced) improves durability.
Smart Surface Treatments:
Antibacterial/Viral Coatings (e.g., silver ion tech) for healthcare/education sectors.
Self-Healing Coatings: Micro-scratch repair for extended lifespan.
Green Adhesives: Water-based/bio-based glues (e.g., soy adhesive) replace solvent-based options.
3. Expanding Applications
Wall panels (alternative to wood cladding), custom furniture (cabinets, countertops).
Outdoor flooring (SPC + weather-resistant wood for patios/balconies).
Automotive/Marine Interiors: Lightweight wood-grain SPC panels.
4. Challenges & Solutions
Cost Competition: SPC is cheaper than solid wood, but premium veneers (e.g., walnut) increase costs—optimize supply chains.
Consumer Perception: Educate buyers via comparative testing to highlight composite advantages over solid wood.
III. Conclusion
SPC-wood composites, driven by smart manufacturing (automated presses) and material innovation (eco-friendly adhesives, high-performance substrates), hold strong potential ingreen construction, premium interiors, and commercial projects. Companies that excel incost efficiency and ultra-realistic wood aesthetics will lead the market.
 consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, new energ
consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, new energ
 Consequences of Inaccurate Adhesive Ratio in Fully Automatic
Consequences of Inaccurate Adhesive Ratio in Fully Automatic
 **Liberating Hands, Intelligent Manufacturing: How Fully Aut
**Liberating Hands, Intelligent Manufacturing: How Fully Aut
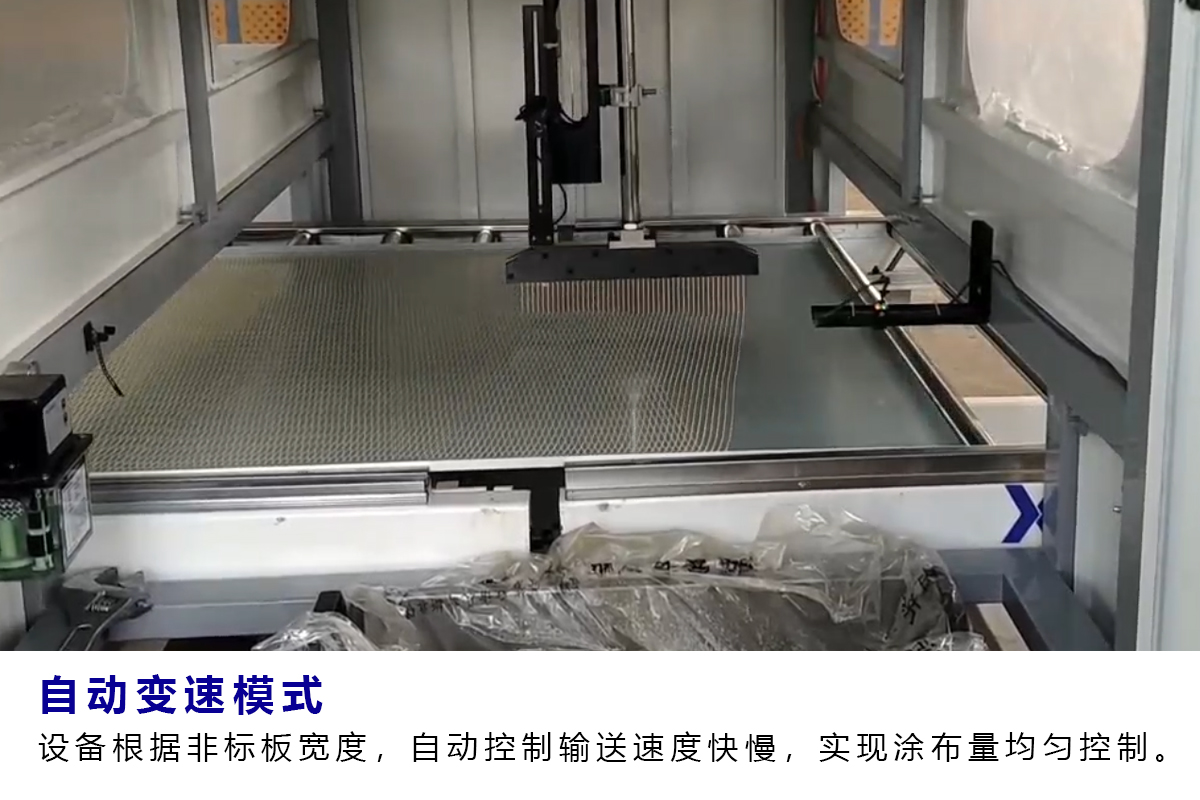 How can a fully automatic glue applicator maintain a consist
How can a fully automatic glue applicator maintain a consist
